How Modern Time Management Is Redefining Personal Success
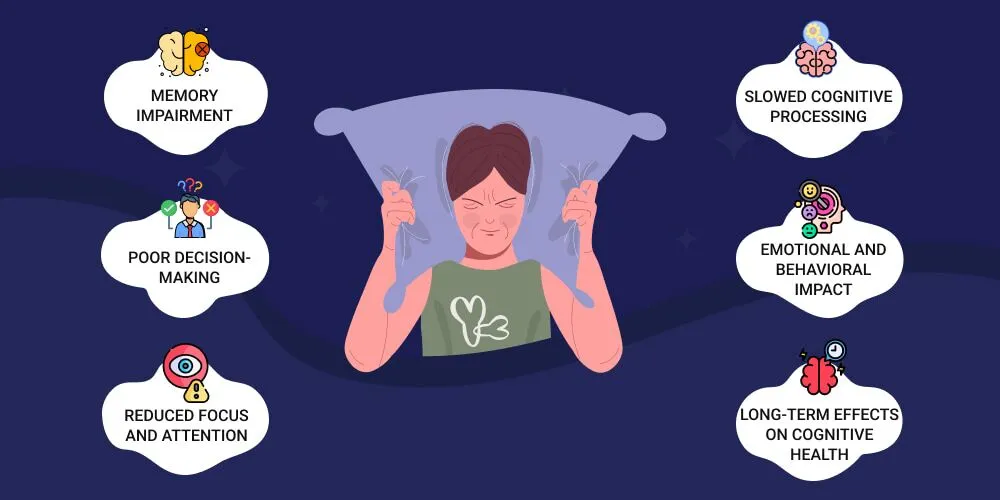
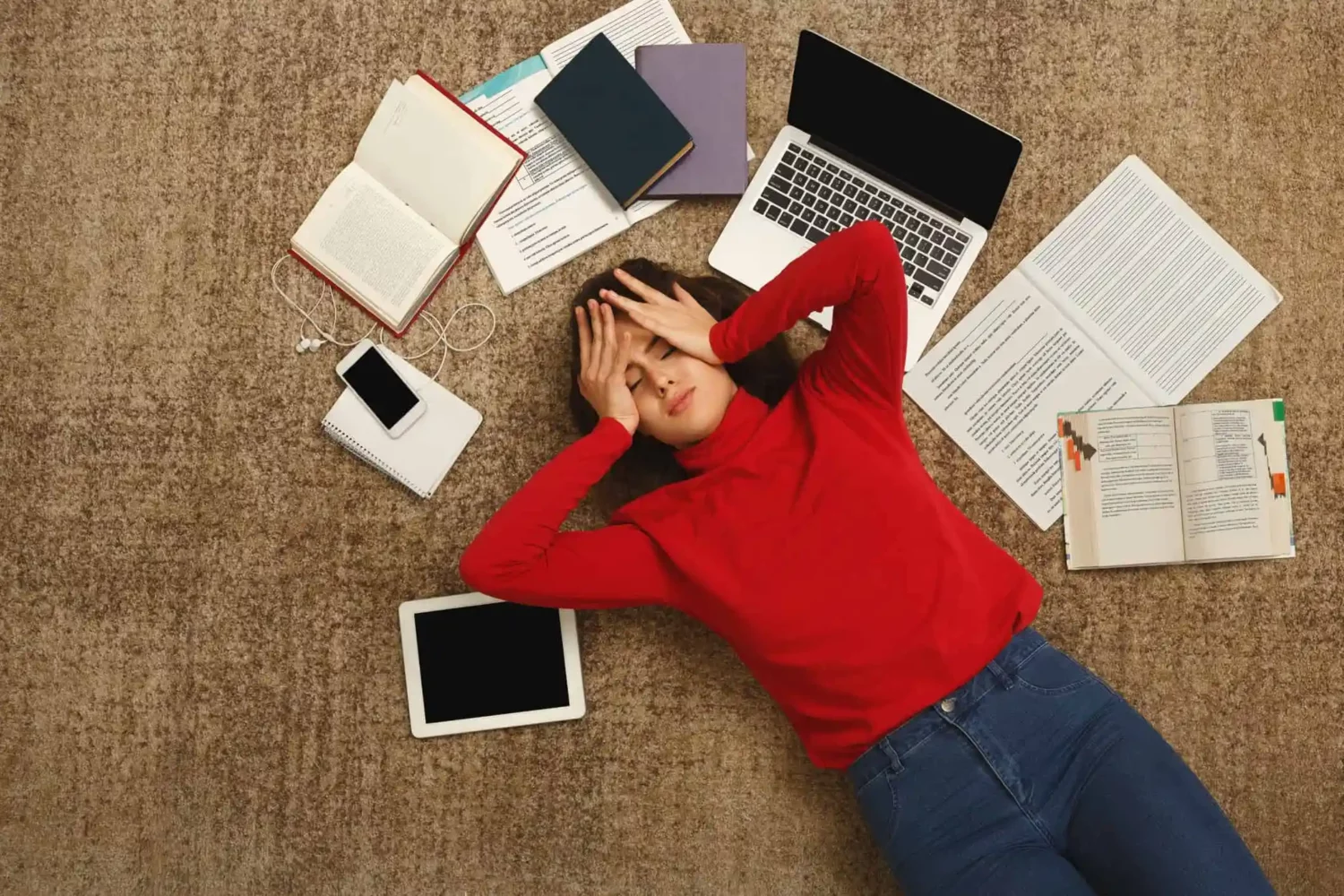
In today’s digital world, time feels more valuable than ever. Constant notifications, deadlines, and responsibilities compete for attention. Effective time management has become a core life skill. Successful people now focus less on working longer hours and more on working intentionally. Setting clear priorities, establishing routines, and scheduling rest are essential strategies for maintaining balance. … Read more